AMD has announced its Ryzen AI MAX+ 395 processor (codenamed “Strix Halo”), positioning it as a high-performing x86 APU for thin and light laptops. The company states the new processor significantly outperforms competitors in AI processing capabilities.
The Ryzen AI MAX+ 395 features AMD’s “Zen 5” CPU cores, an XDNA 2 Neural Processing Unit (NPU) with over 50 peak AI TOPS, and an integrated GPU based on AMD RDNA 3.5 architecture with 40 Compute Units. This combination aims to provide a substantial upgrade for premium thin and light laptops, offering memory configurations from 32GB up to 128GB of unified memory. Notably, up to 96GB of this memory can be allocated as VRAM through AMD Variable Graphics Memory.
AMD highlighted the processor’s capabilities in handling consumer AI workloads, specifically mentioning the llama.cpp-powered application LM Studio. This application allows users to run large language models (LLMs) locally without requiring specialized technical knowledge, simplifying the deployment of new AI text and vision models.
According to internal benchmarks conducted by AMD using an ASUS ROG Flow Z13 laptop equipped with 64GB of unified memory and an integrated Radeon 8060S GPU, the Ryzen AI MAX+ 395 demonstrated up to 2.2 times the token throughput of a laptop with an Intel Arc 140V graphics card. The tests focused on LLMs that could fit within 16GB of memory to ensure compatibility with competing laptops featuring 32GB of on-package memory.
The performance advantage reportedly remained consistent across various model types, including chain-of-thought models like DeepSeek R1 Distills and standard models such as Microsoft Phi 4, as well as across different parameter sizes.
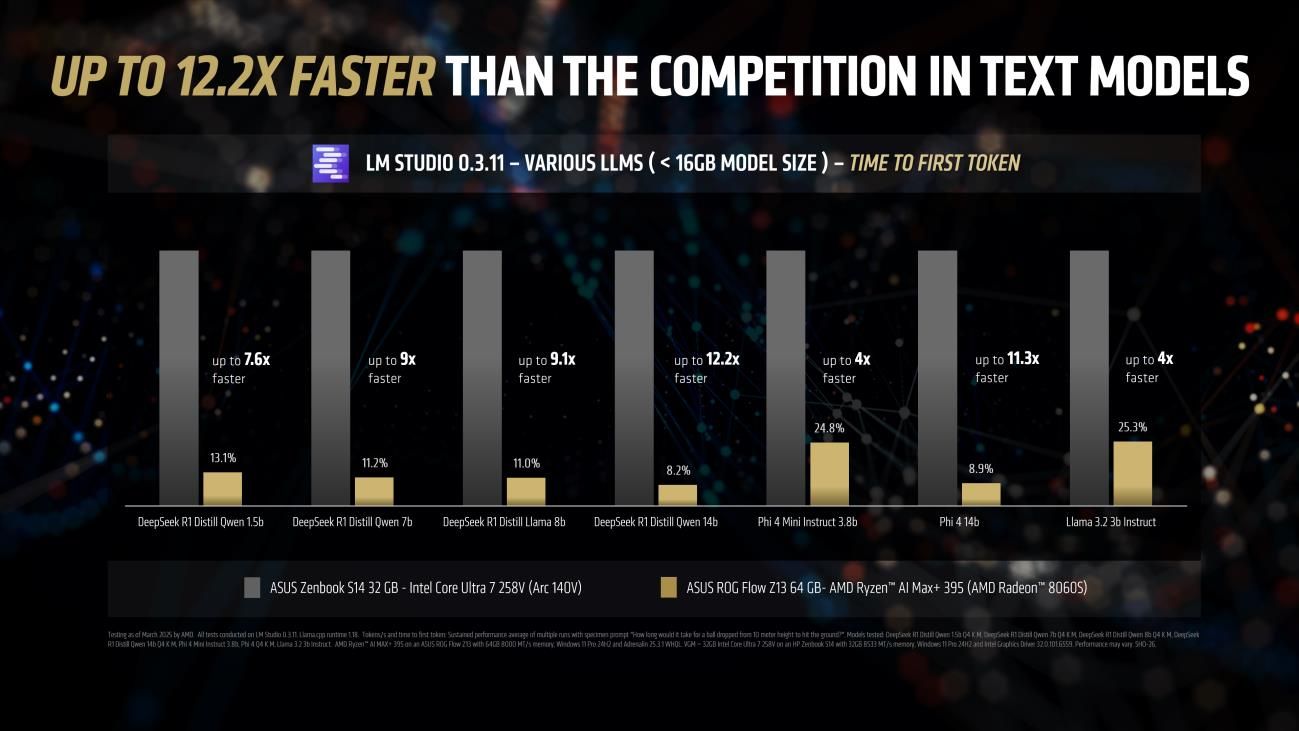
In terms of time to first token, a metric indicating the responsiveness of the model, the AMD Ryzen™ AI MAX+ 395 processor showed even greater gains. For smaller models like Llama 3.2 3b Instruct, it was up to four times faster than the competition. For larger 7 billion and 8 billion parameter models like DeepSeek R1 Distill Qwen 7b and DeepSeek R1 Distill Llama 8b, the speed increase was reported to be as high as 9.1 times. When testing with 14 billion parameter models, the ASUS ROG Flow Z13, powered by the Ryzen AI MAX+ 395, was reportedly up to 12.2 times faster than a laptop with an Intel Core Ultra 258V processor.
AMD also presented data on the processor’s performance with multi-modal models that incorporate vision capabilities, such as IBM Granite Vision and Google Gemma 3. In these tests, the Ryzen AI MAX+ 395 processor showed significant speed advantages in the time taken for the model to analyze an image and provide a response. For instance, it was reported to be up to seven times faster in IBM Granite Vision 3.2 3b, up to 4.6 times faster in Google Gemma 3 4b, and up to six times faster in Google Gemma 3 12b. The ASUS ROG Flow Z13 with 64GB of memory was also able to run the larger Google Gemma 3 27B Vision model.
A demonstration showcased the potential of these vision models, where a model identified organs and provided a diagnosis from a stock CT scan image. AMD also highlighted the ability to run large language models for coding tasks, such as running DeepSeek R1 Distill Qwen 32b in 6-bit precision to code a simple game like Pong in a short timeframe.
To optimize performance for LLM workloads on laptops with Ryzen AI 300 series processors, AMD recommends updating to the latest AMD Software: Adrenalin Edition driver and enabling Variable Graphics Memory (VGM) with a setting of High. This feature allows the system to dynamically allocate memory to the integrated graphics, improving token throughput and enabling the use of larger AI models. AMD also suggests specific settings within LM Studio, such as manually selecting parameters and setting GPU Offload to MAX, along with recommending Q4 K M quantization for general use and Q6 or Q8 for coding tasks.
The AMD Ryzen AI MAX+ 395 processor aims to provide users with a portable platform for experiencing advanced AI models on thin and light laptops, suitable for both gaming and productivity.